15 4月 Degassing Aluminum Indonesia
Degassing Aluminum Indonesia
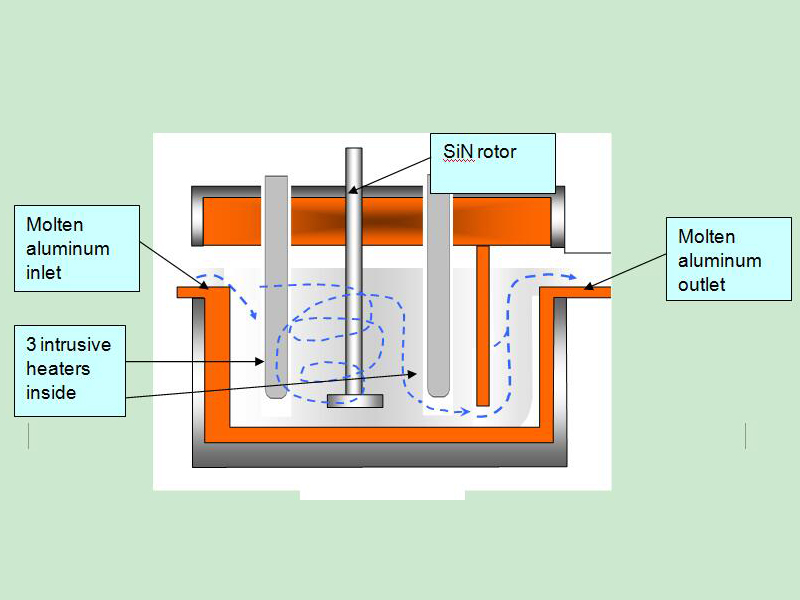
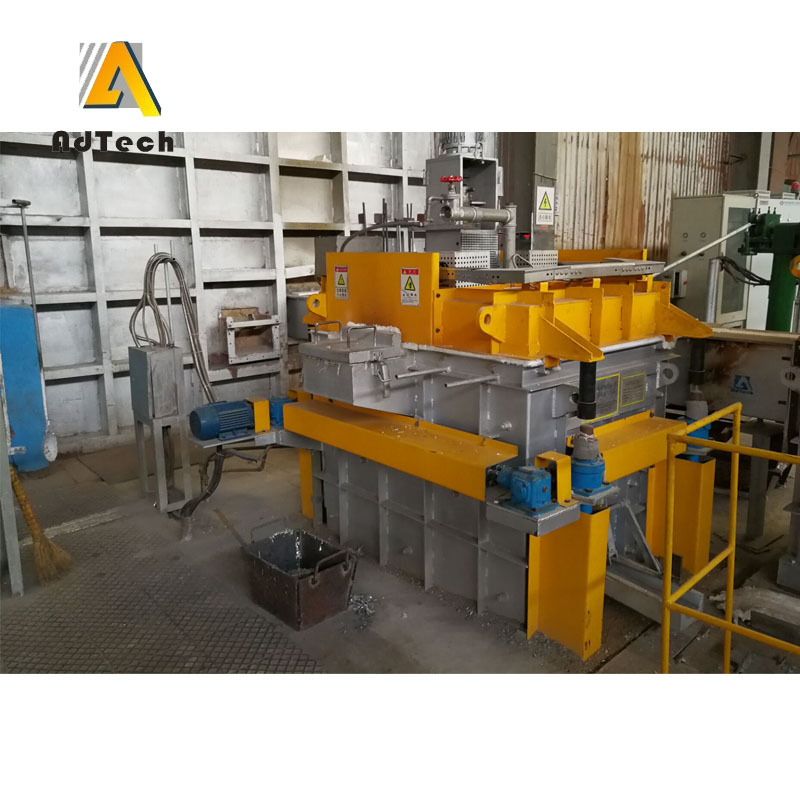
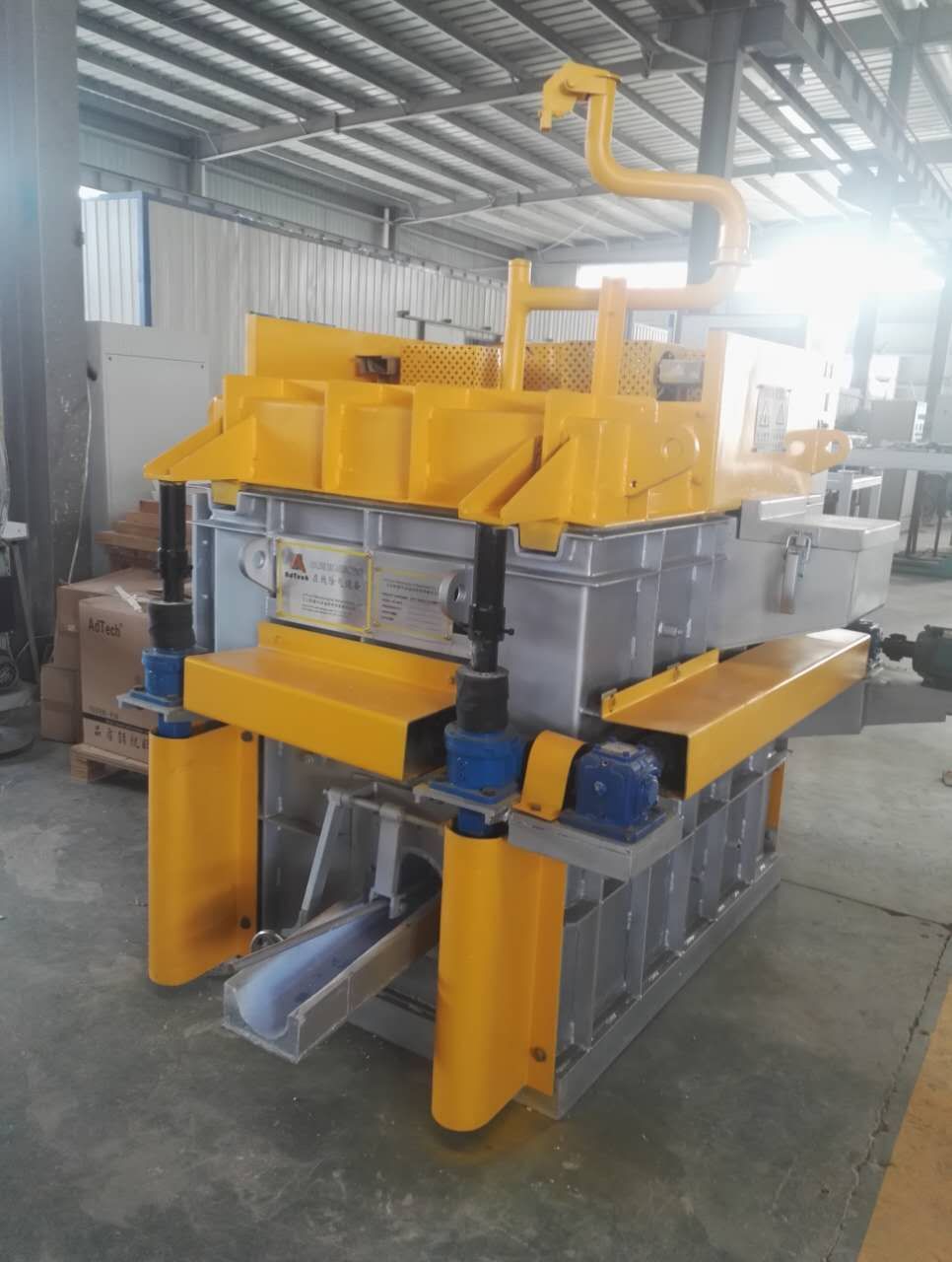
Degassing Aluminum Indonesia In the rotary degassing method an inert or chemically inactive gas (Argon, Nitrogen) is purged through a rotating shaft and rotor.
Energy of the rotating shaft causes formation of a large number of fine bubbles providing very high surface area-to volume ratio.
Large surface area promotes fast and effective diffusion of hydrogen into the gas bubbles resulting in equalizing activity of hydrogen in liquid and gaseous phases.
Rotary Degassing Aluminum Indonesia allows achieve more complete hydrogen removal as compared to the flux degassing.
Additionally rotary degasser does not use harmful chlorine and fluorine containing salts.
Rotary Degassing Aluminum Indonesia may also combine the functions of degassing and flux introduction.
In this case the inert gas serves as carrier for granulated flux. The method is called flux injection.
Advantages of flux injection
high effectiveness of flux action due to better mixing with the melt;
short flux treatment time;
controllable flux introduction;
more environmentally friendly method of fluxing.

Sources of hydrogen in molten aluminum
atmosphere humidity;
wet metallic charge;
wet furnace lining (crucible, transfer ladles);
wet foundry instruments;
wet fluxes and other consumables;
furnace fuel combustion products containing hydrogen.

Methods of hydrogen content estimation
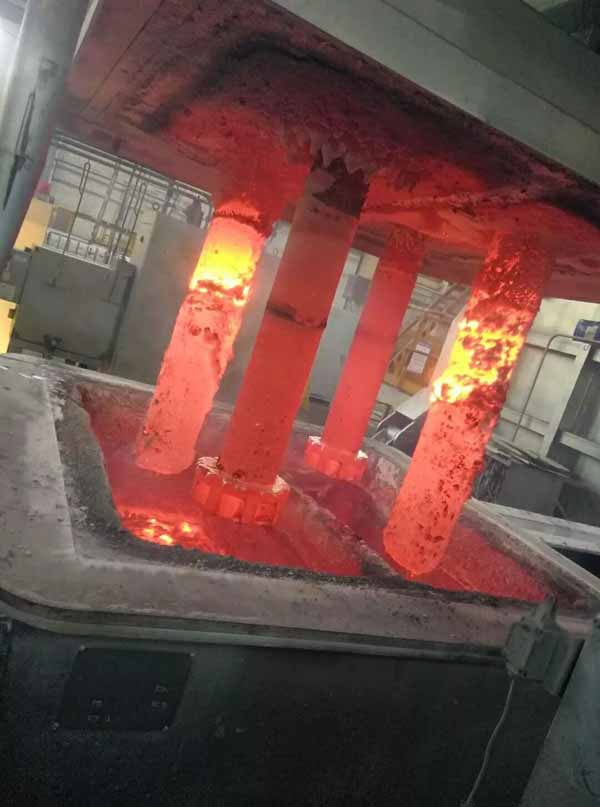
Slow solidification. In this method a small portion of liquid aluminum (about 2 in3/33 cm3) is poured into a cavity in a heated refractory brick. The alloy slowly solidifies and the released hydrogen is concentrated in the upper part of the casting in form of frozen bubbles. Quantity of the hydrogen bubbles at the sample surface is determined by the hydrogen concentration.
Vacuum method. This quantitative method uses solidification of a sample portion of the aluminum alloy in a small crucible at low pressure. Hydrogen dissolved in the alloy starts to form a gaseous phase (a bubble) at a certain pressure. When the first bubble is formed both the pressure and the temperature are measured. These parameters are used for determination of the hydrogen content by means of numeric diagrams.
Degassing by fluxes
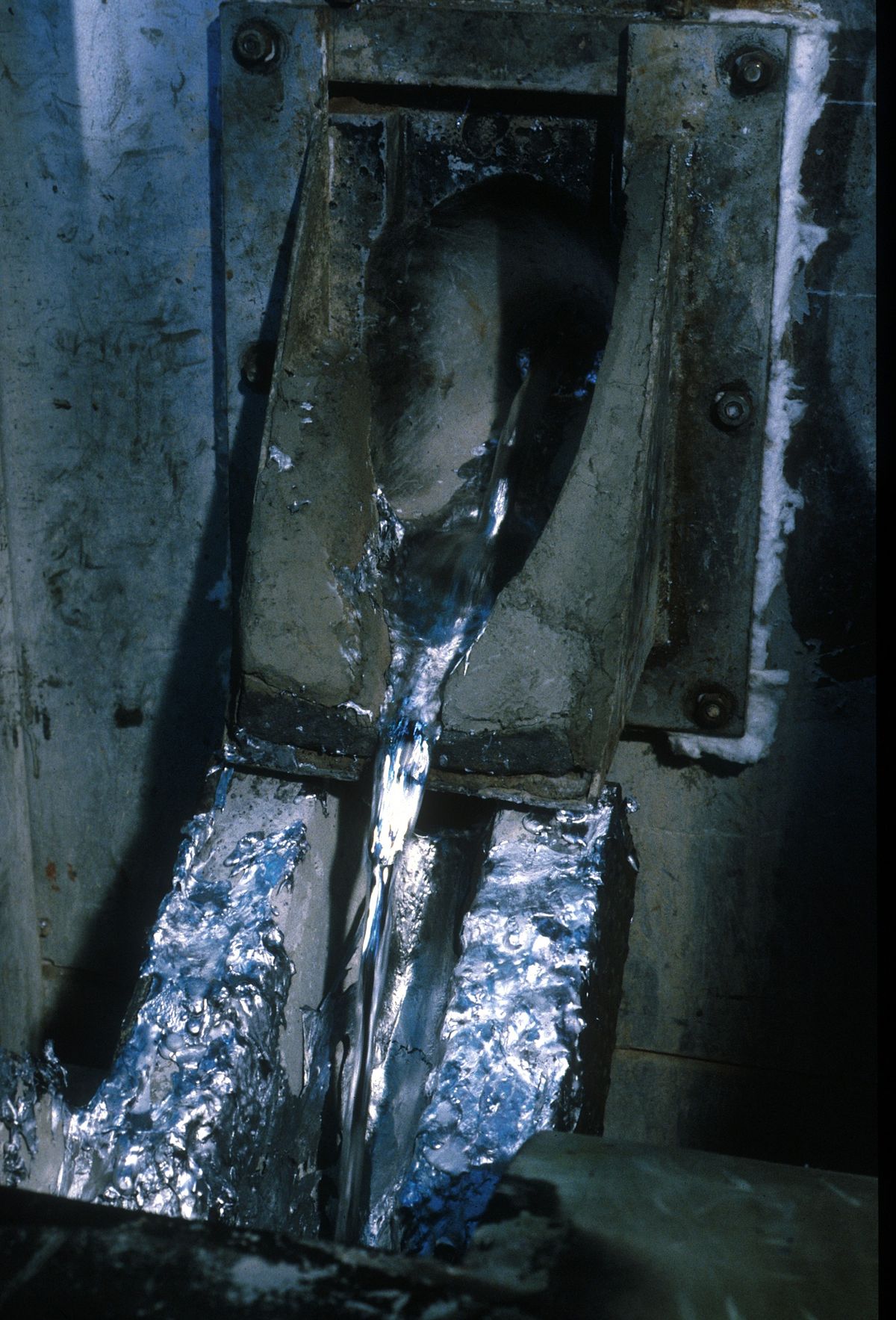
Fluxes composed of chlorine and fluorine containing salts are used for degassing molten aluminum alloys. Degassing fluxes are commonly shaped in form of tablets.
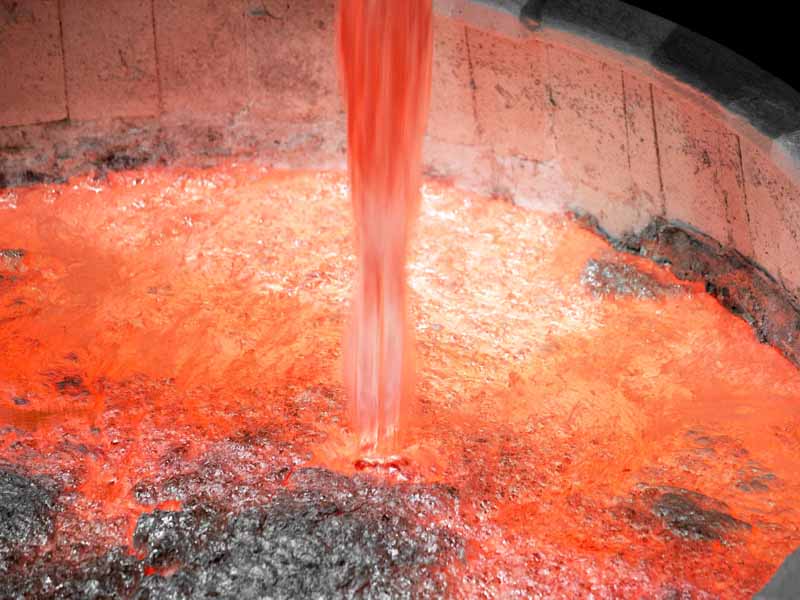
Degassing operation starts when a flux tablet is plunged by a clean preheated perforated bell to the furnace bottom. The flux components react with aluminum forming gaseous compounds (aluminum chloride, aluminum fluoride). The gas is bubbling and rising through the melt. Partial pressure of hydrogen in the formed bubbles is very low therefore it diffuses from the molten aluminum into the bubbles. The bubbles escape from the melt and the gas is then removed by the exhausting system.
The process continues until bubbling ceases.













No Comments