20 Dec Aluminum melting process
Aluminum melting process
Aluminum melting process
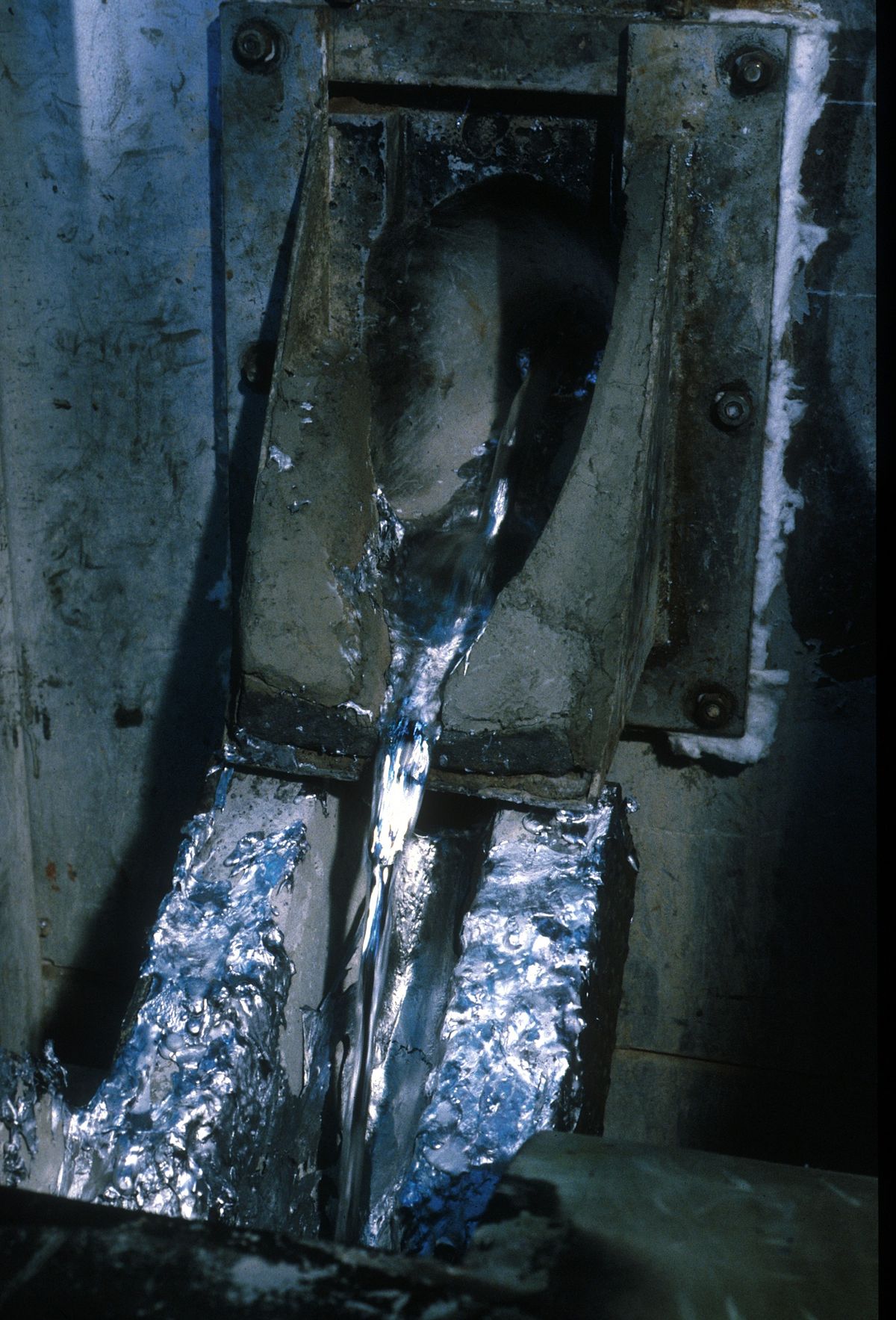
Charging of aluminum melting furnace → smelting (adding copper, zinc, silicon, etc.) → slag removal → adding magnesium, beryllium, etc. → stirring → sampling → adjusting ingredients → stirring → refining → slag removal → converter → refining deterioration and standing → casting.
Assembly of induction smelting furnace:
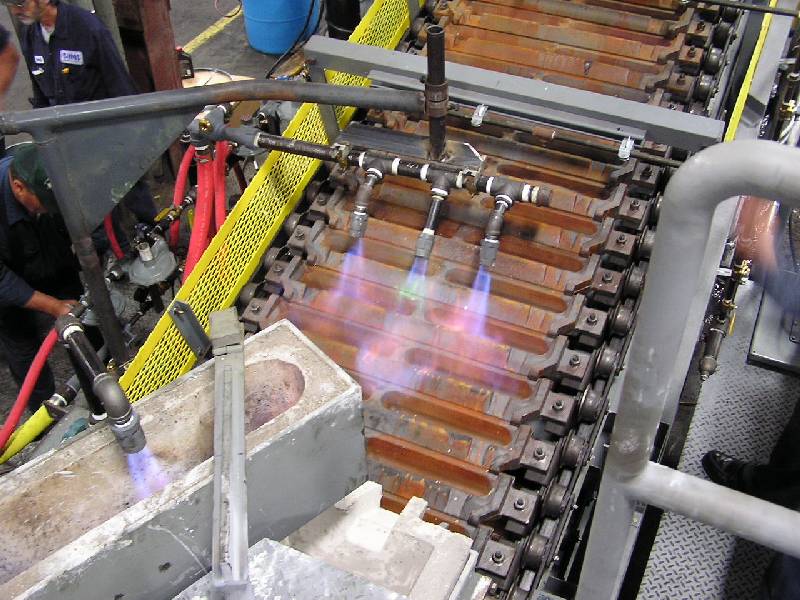
The correct charging method is essential to reduce metal burnout and shorten smelting time.
For a reverberatory furnace, lay a layer of aluminum ingots on the bottom of the furnace, put in combustibles, and then press the aluminum ingots into the furnace. Put the reflux material with a lower melting point on the upper layer to melt it as soon as possible, and cover the lower layer with easy fuel to reduce burnout. Various furnace charges should be evenly distributed.
Smelting:
The smelting process and melting speed have an important influence on the quality of aluminum ingots.
When the furnace charge is heated to the softened material layer, the flux should be properly covered.
During the smelting process, care should be taken to prevent overheating. After the charge is melted to a flat surface, the melt should be stirred appropriately to make the temperature uniform, which is also conducive to accelerating smelting.
Long smelting time will not only reduce the furnace production efficiency, but also increase the gas content of the melt. Therefore, when the smelting time is too long, the melt should be re-refined.

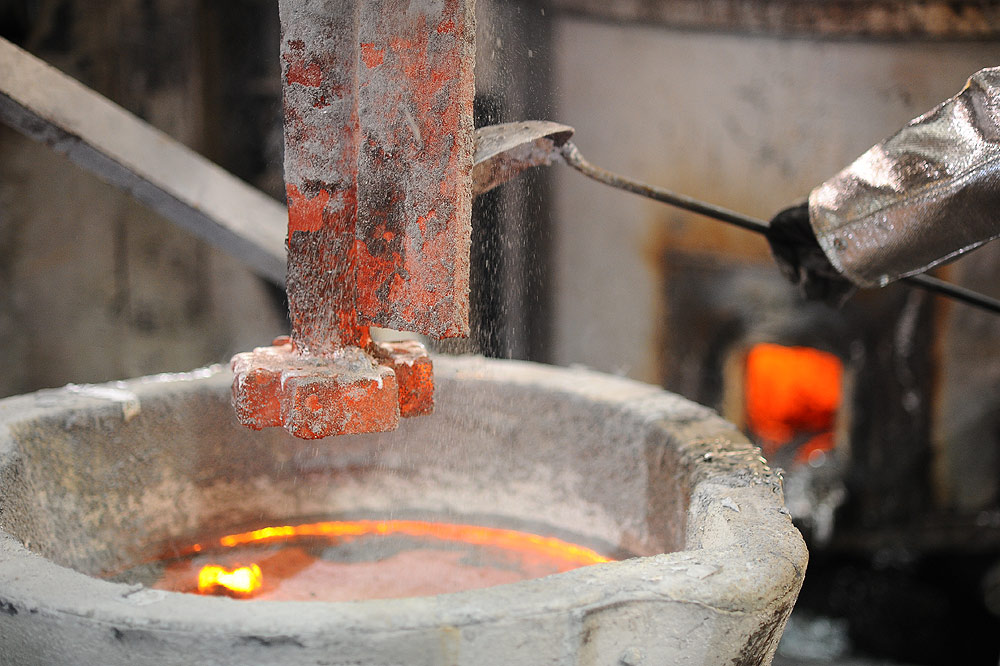
Slag removal:
After all the charge is melted to the melting temperature, slag removal can be carried out. Dust removal powder should be sprinkled before picking up the slag (high magnesium alloy should be sprinkled with sodium-free flux). Slag scraping should be as thorough as possible, because slag is easy to contaminate metal and increase the gas content of the melt.
After adding magnesium-beryllium slag, magnesium ingots can be added to the melt and covered with flux. To prevent magnesium burning, high magnesium alloys should add 0.002% to 0.02% beryllium. Beryllium can be obtained by the metal reduction of sodium beryllium fluoride. Sodium beryllium fluoride is mixed with flux.
Stirring:
Sufficient stirring time should be left before sampling and after adjusting the ingredients. The stirring should be stable and not damage the oxide film on the surface of the melt.
Sampling:
After the melt is fully stirred, it should be sampled and analyzed immediately in front of the furnace.
Adjust the ingredients: When the ingredients do not meet the standard requirements, they should be supplemented or diluted.
Melt converter:
Adjust the ingredients, and after the melt temperature reaches the requirements, remove the surface slag and then convert it.
Melt refining:
Different metamorphic components have different purification methods (Aidetai Metallurgical Materials Co., Ltd. has been focusing on the research and development, production, and marketing of bonded ceramic foam filters (CFF) and aluminum liquid degassing equipment for aluminum alloy casting since 2012), metamorphic methods, and refining flux.















Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.