
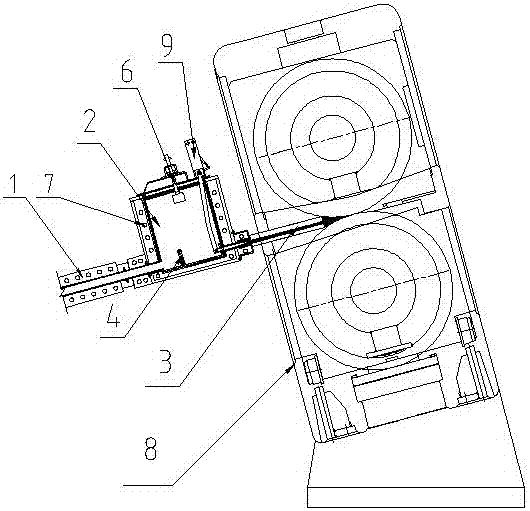
17 12月 Feeder Tip Cavity
Feeder Tip Cavity is used for the crystal forming and size control of aluminum sheet, strip and foil blanks in the casting and rolling production line. It is formed by vacuum suction and filtration of nano-fiber composite materials and processed by high-precision CNC machine tools.
Feeder Tip Cavity has uniform distribution of internal short fiber structure, moderate density, good heat preservation, precise size, high oxidation resistance, no delamination and no block, low deformation, effective protection of the quality of cast-rolled coils, and nitriding The effect of boron paint is better.

Advantages and disadvantages of continuous casting and rolling
advantage:
A. Because the thickness of the continuous casting and rolling slabs is thin and can be rolled directly with waste heat, it saves high-power hot rolling mills, ingot heating equipment and milling equipment;
B. The production line is simple and centralized. From smelting to rolling out of the strip, the product can be continuously carried out in one production line, which simplifies many intermediate processes such as ingot sawing, milling, heating, hot rolling, and transportation, and simplifies the production process. , Shorten the production cycle;
C. Less geometric waste and high yield;
D. High degree of mechanization and automation;
E. Less equipment investment and low production cost.
Disadvantages:
A. There are few alloys that can be produced, especially alloys with a large crystallization temperature range;
B. Product varieties and specifications are not easy to change frequently;
C. Since the surface of the ingot cannot be milled and trimmed, it will have an adverse effect on some products that require chemical treatment and high surface requirements;
D. Due to performance limitations, some special products cannot be produced, such as canned materials;
E. The output is restricted. If the scale of production needs to be expanded, the only way to increase the number of production lines.
The function of the aluminum casting-rolling mill is to cast-roll primary aluminum into cast-rolled alloy strips suitable for cold rolling.
The specific process requires that molten aluminum for casting and rolling must be continuously supplied.
Aluminum alloy melt must be clean, and have consistent chemical composition, and require constant liquid level and temperature.
The constant liquid surface between the furnace and the aluminum casting and rolling mill is essential for the smooth operation of the rolling line.
The liquid level is kept constant by a simple orifice flow control device by adjusting the outlet flow.
Between the melting furnace and the casting and rolling mill, two aluminum titanium boron wires are inserted into the launder system.
The wire is fed by a titanium wire feeder at a predetermined constant speed.
The pure molten aluminum, which maintains a constant level and temperature, then flows into the front box of the casting mill.
The combination of the unique 15° inclination angle of the casting and rolling mill and the precise control device in the headbox allows the headbox to supply Castertip with molten aluminum under extremely precise pressure.
Through the nozzle of Castertip, the aluminum liquid can be injected into the roll cooled by the cooling water. The aluminum liquid is distributed along the width of the roll surface, and then the aluminum liquid is cooled and solidified.
At this time, the metal is in the roll gap slightly ahead of the centerline of the rolls of the cast-rolling mill, and then it is hot rolled to shape it.
The cast aluminum is formed into cast-rolled strip after hot rolling.
Each roll of the aluminum casting mill is driven by a DC motor and a planetary gear reducer, and the synchronous control is carried out by an advanced digital control system.
The surface of the casting roll is continuously sprayed with a graphite solution with separation and lubrication effects.
After the aluminum cast-rolled strip leaves the roll gap, it passes through the lead-out roll and then moves forward along the rolling line. Finally, it passes through the deflector roll and is coiled by a down-coiler driven by a DC motor.
The coiler can maintain the tension of the cast-rolled strip.
When the strip size meets the requirements, the strip should be cut without stopping the casting and rolling.
In order to complete the operating process of the cast-rolling mill, the system is equipped with a set of hydraulically driven pinch rolls to maintain the tension at the exit of the cast-rolling mill.
The pinch roller is clamped before the synchronous shearing machine cuts and is opened immediately after the roll is changed.















Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.