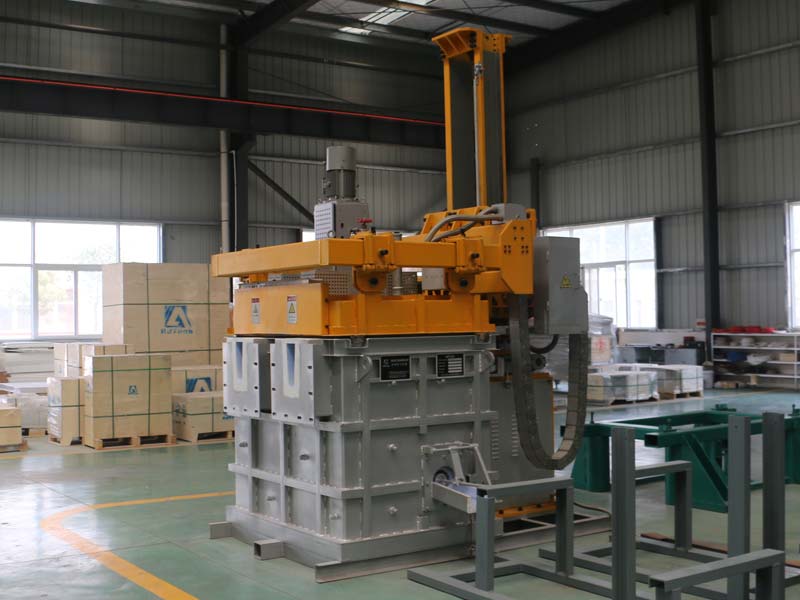

09 8月 Degassing In Foundry
Degassing In Foundry
Classification of cast aluminum alloys is developed by the Aluminum Association of the United States:
Each cast alloy is designated by a four digit number with a decimal point separating the third and the forth digits.
The first digit indicates the alloy group according to the major alloying element:
1xx.x aluminum, 99.0% minimum;
2xx.x copper (4%…4.6%);
3xx.x silicon (5%…17%) with added copper and/or magnesium;
4xx.x silicon (5%…12%);
5xx.x magnesium (4%…10%);
7xx.x zinc (6.2%…7.5%);
8xx.x tin;
9xx.x others.

The second two digits identify aluminum alloy or indicate the alloy purity.
In the alloys of the 1xx.x series the second two digits indicate the level of purity of the alloy – they are the same as the two digits to the right of the decimal point in the minimum concentration of aluminum (in percents): 150.0 means minimum 99.50% of aluminum in the alloy, 120.1 means minimum 99.20% of aluminum in the alloy.
In all other groups of aluminum alloys (2xx.x through 9xx.x) the second two digits signify different alloys in the group.
The last digit indicates the product form: casting (designated by “0”) or ingot (designated by “1” or “2” depending on chemical composition limits.)
A modification of the original alloy or impurity limits is indicated by a serial letter before the numerical designation. The serial letters are assigned in alphabetical order starting with A but omitting I, O, Q, and X (the letter “X” is reserved for experimental alloys).
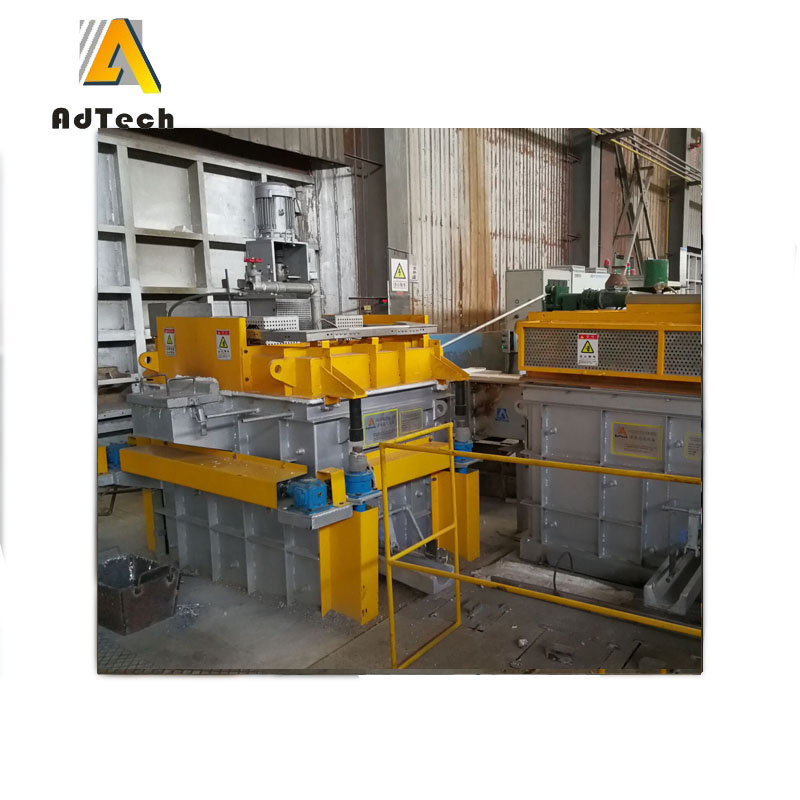
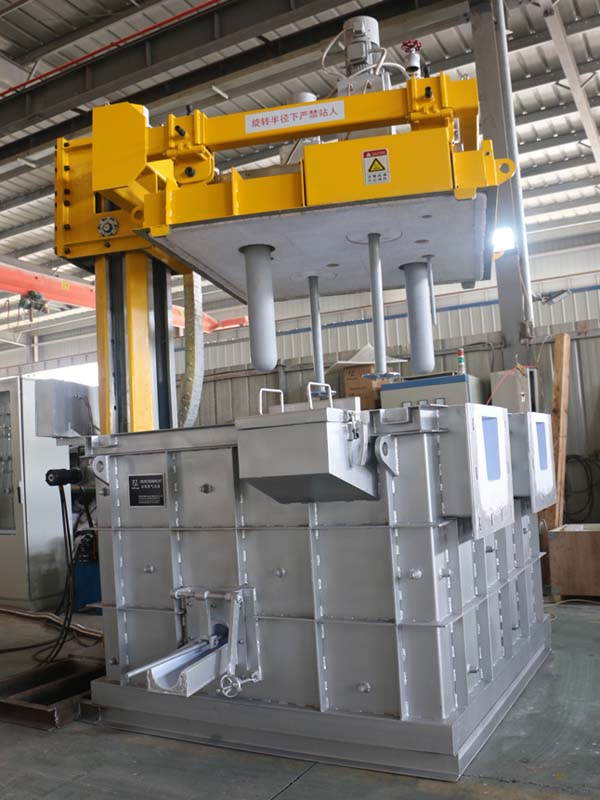
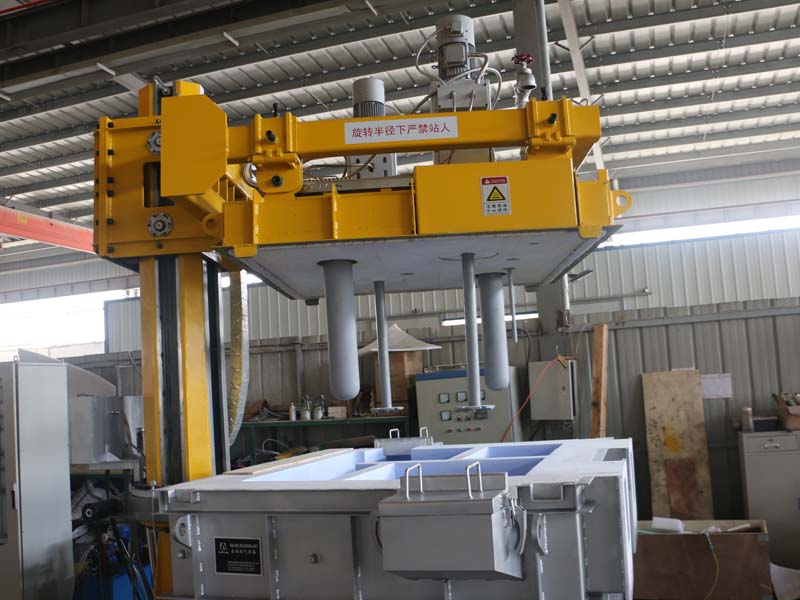
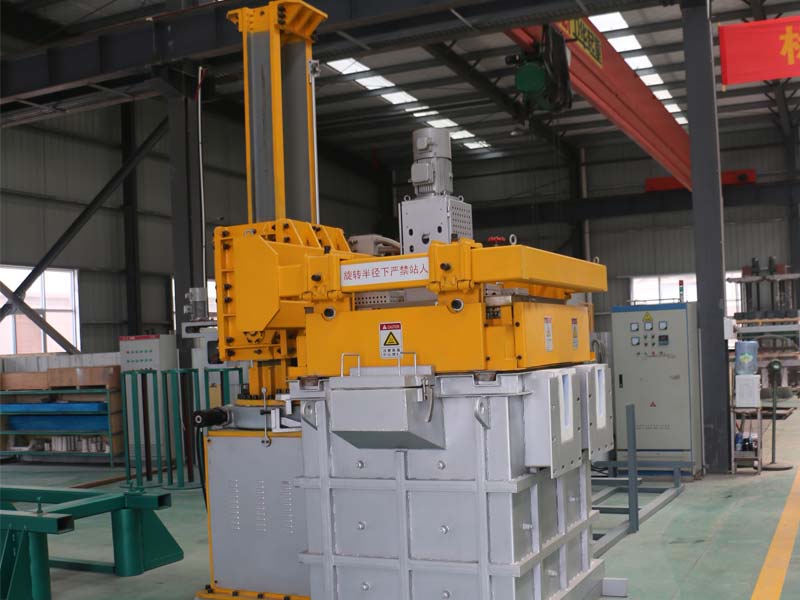
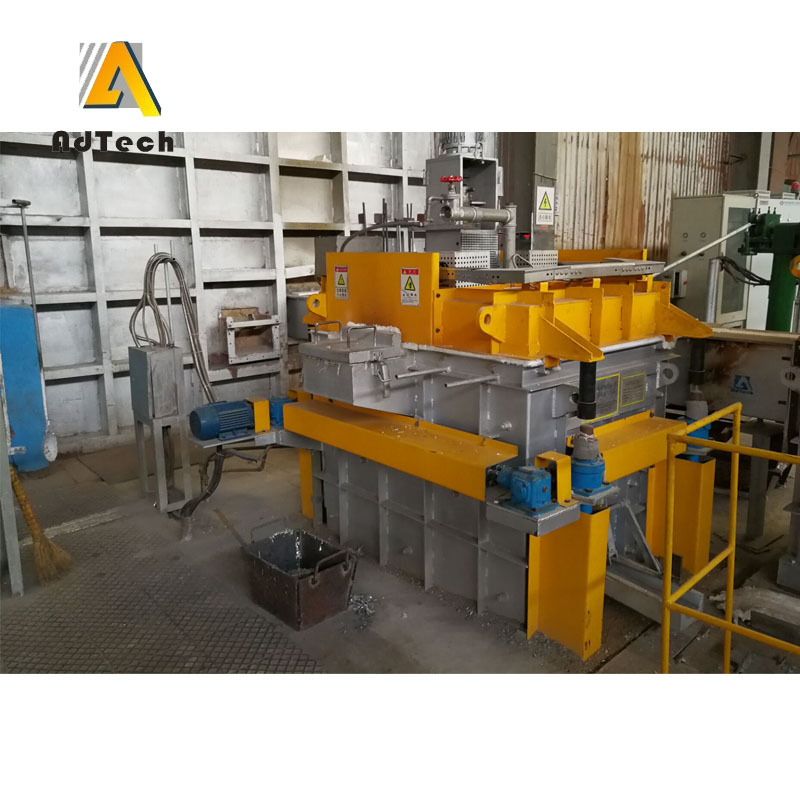
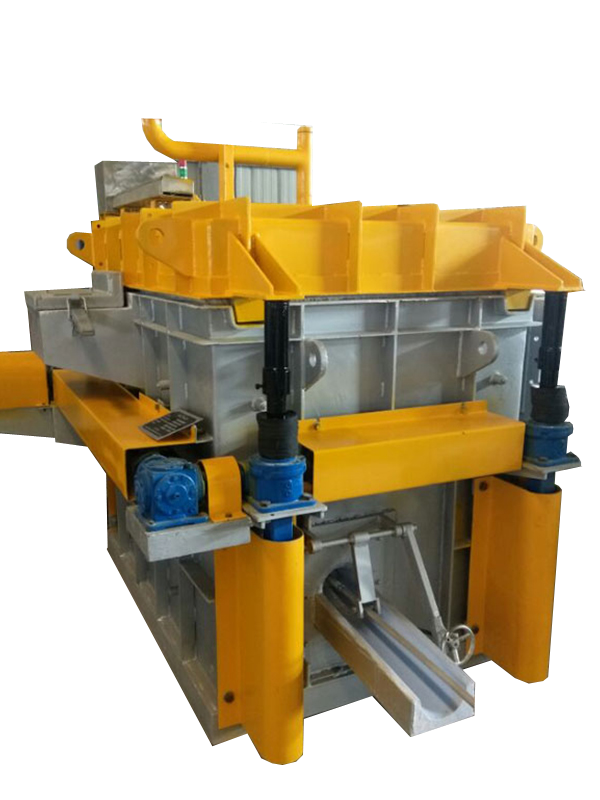
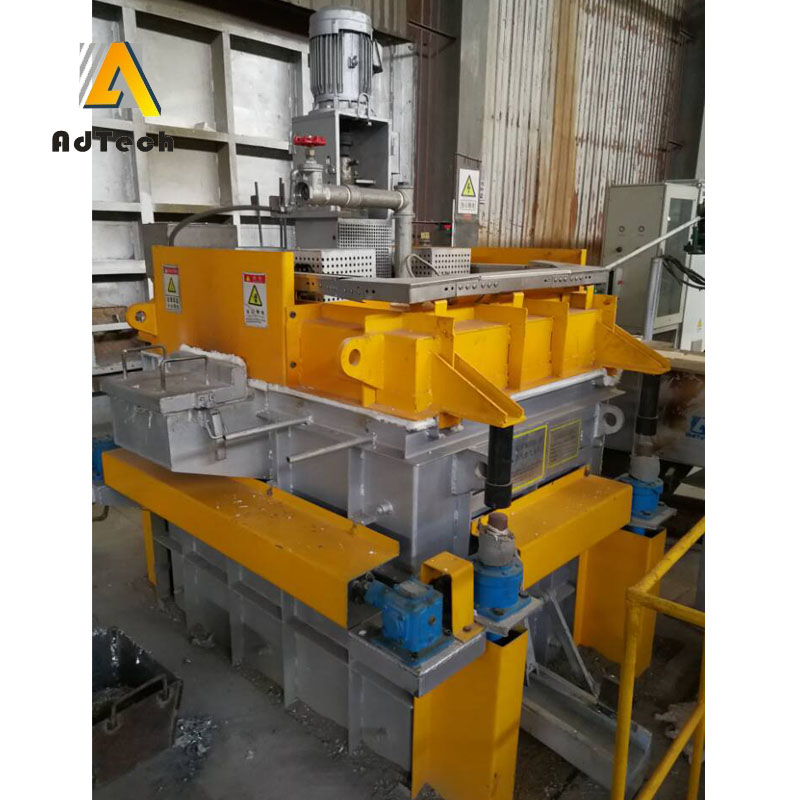
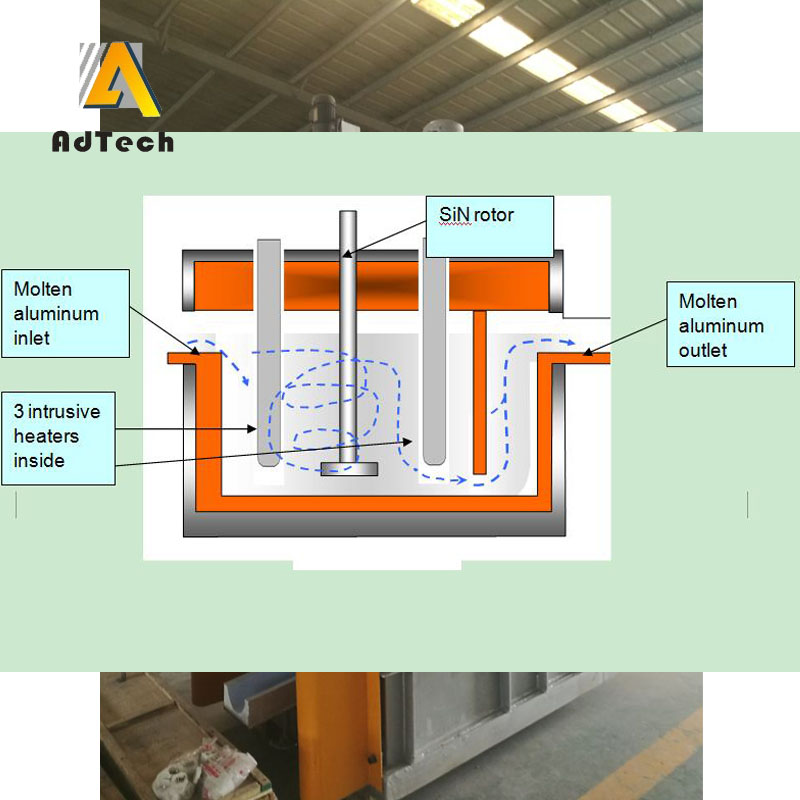
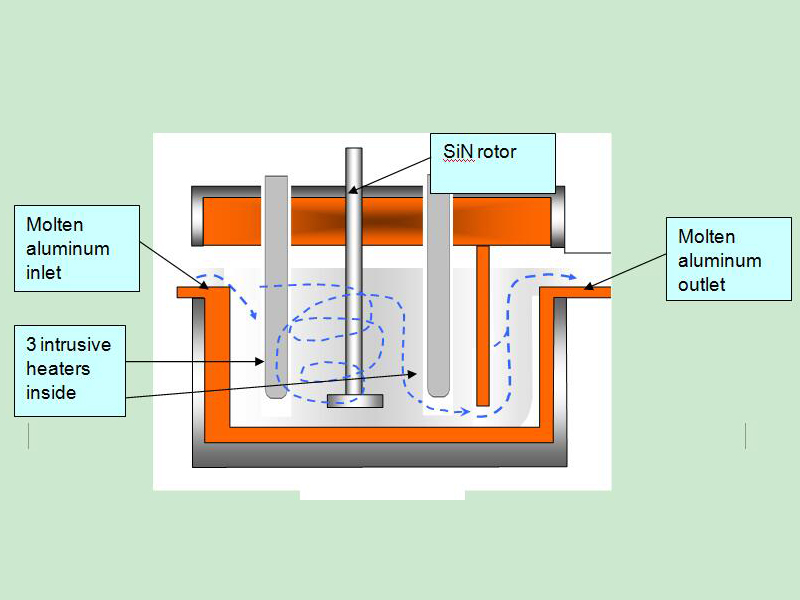
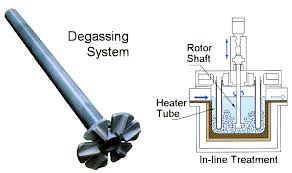
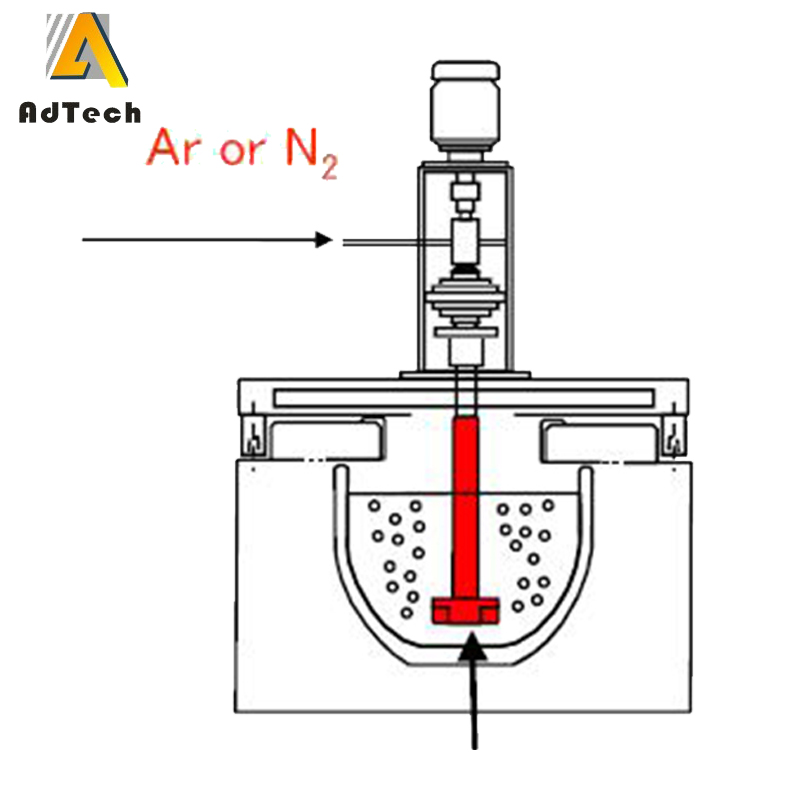
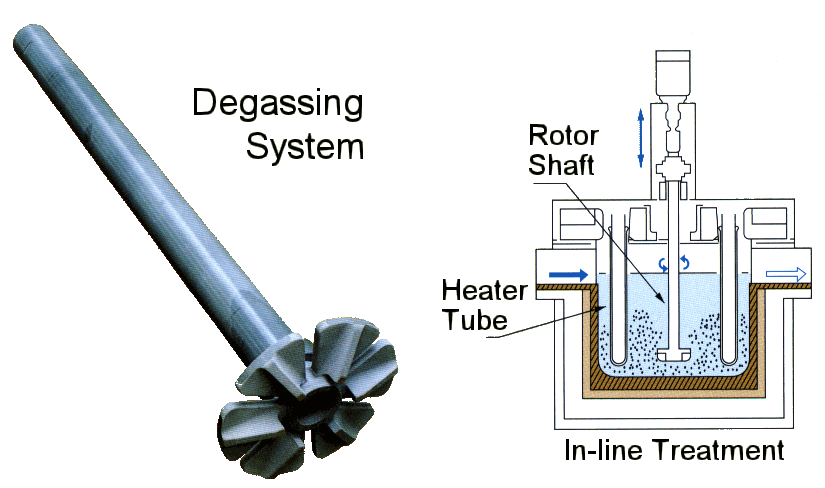
Degassing In Foundry, an inert or chemically inactive gas (Argon, Nitrogen) is purged through a rotating shaft and rotor.
Energy of the rotating shaft causes formation of a large number of fine bubbles providing very high surface area-to volume ratio.
Large surface area promotes fast and effective diffusion of hydrogen into the gas bubbles resulting in equalizing activity of hydrogen in liquid and gaseous phases.
Rotary Degassing In Foundry allows achieve more complete hydrogen removal as compared to the flux degassing.
Additionally rotary degasser does not use harmful chlorine and fluorine containing salts.
Rotary degasser may also combine the functions of degassing and flux introduction in Degassing Aluminum Casting Process
In this case the inert gas serves as carrier for granulated flux. The method is called flux injection.










Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.