
19 6月 Aluminum Ingot Continuous Casting Degassing Aluminum With Argon
Aluminum Ingot Continuous Casting Degassing Aluminum With Argon
What is the basic principle of Argon gas rotary blowing and Degassing Aluminum With Argon aluminum alloy liquid?
Nitrogen gas is ejected from the graphite nozzle of the rotary degasser and floats up in the aluminum liquid.
Degassing Aluminum With Argon is the purpose of spraying Nitrogen into molten aluminum to remove hydrogen.
In addition, degassing is also considered to be a very effective way to float impurities.
Two main theoretical modes have been proposed to explain the principle of degassing. The macro mode considers that the removal of each impurity is similar in nature. The microscopic mode, that is, according to this theory, due to the higher vapor pressure of hydrogen, the dissolved hydrogen diffuses into the gas in the injected aluminum liquid.
Theoretically, an inclusion having a diameter of 10 microns contacts a bubble and is adsorbed on the bubble and floats up to the surface of the liquid.
The hydrogen partial pressure in the nitrogen bubble just emerging from the graphite nozzle is 0. When the nitrogen floats, the hydrogen diffuses from the aluminum liquid into the nitrogen bubble under the driving force of the hydrogen pressure difference, and the process until the hydrogen partial pressure in the nitrogen bubble When the hydrogen partial pressure in the aluminum liquid is balanced, the nitrogen phase is stopped, and then the nitrogen gas is floated up to the surface to be removed, thereby degassing.
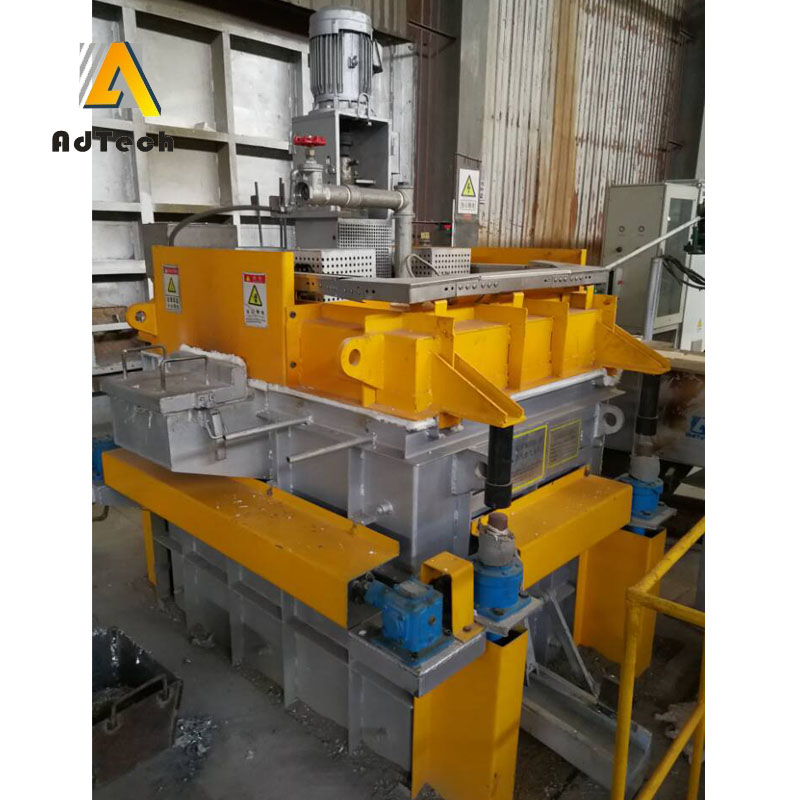
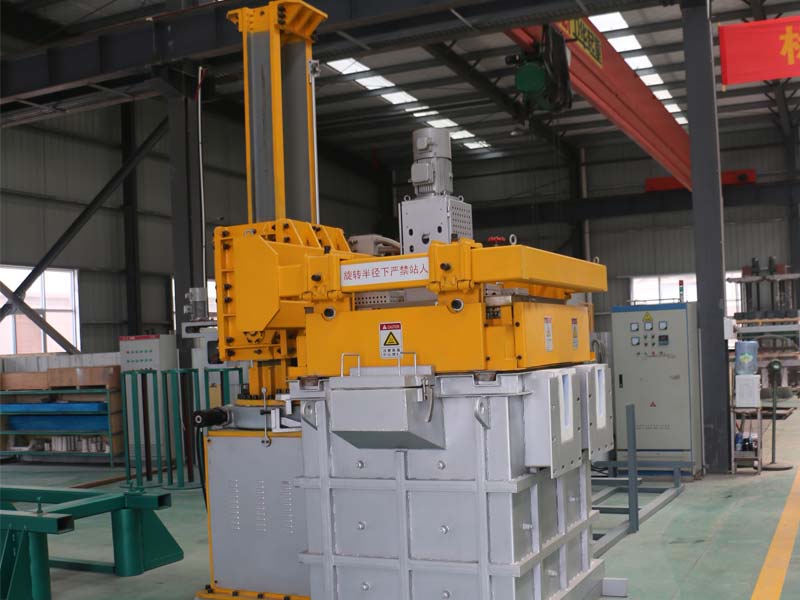
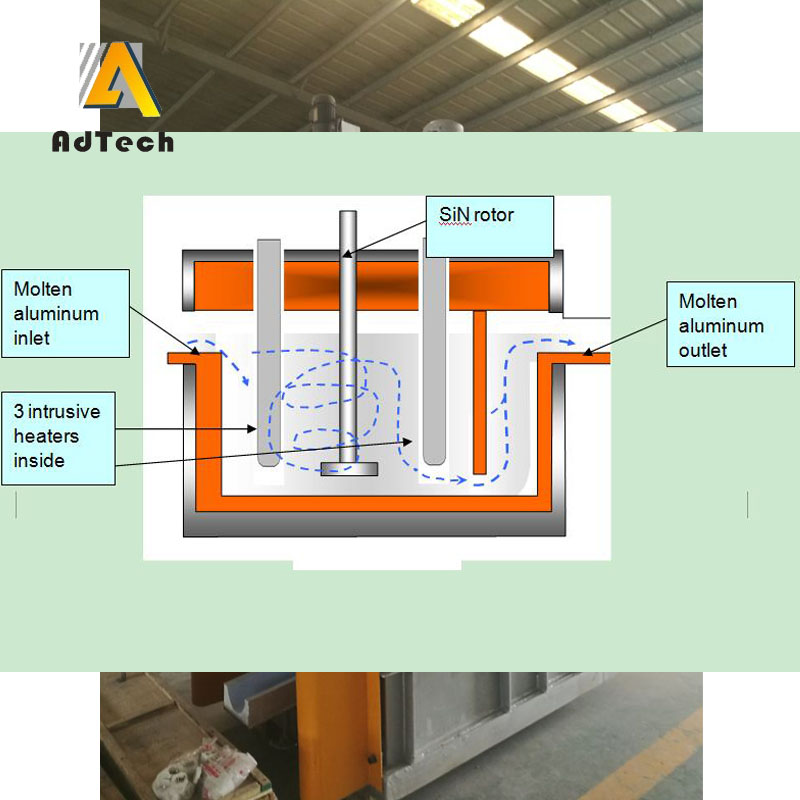
Degassing Aluminum With Argon bubbles by improving the rotating nozzle in the process of purifying nitrogen purification, and increased the contact area between Argon and aluminum, thereby improving the effect of degassing and slag removal, and achieving the purpose of aluminum purification. Improve the quality of the product.
The key to Degassing Aluminum With Argon is that the rotor can break up the incoming Argon bubbles into small bubbles and spread them throughout the molten metal. By reducing the bubble diameter, the surface area of Argon is drastically increased, so that more Argon surface contacts the hydrogen and impurities in the molten metal and the hydrogen or impurities are removed from the aluminum liquid as the bubbles rise.
The flow control into the aluminum Argon can adjust the flow rate of the gas according to the volume of the metal liquid being treated, and the speed of the rotating rod and the rotor can be adjusted to produce a bubble of an appropriate size to facilitate the diffusion of the inert gas.

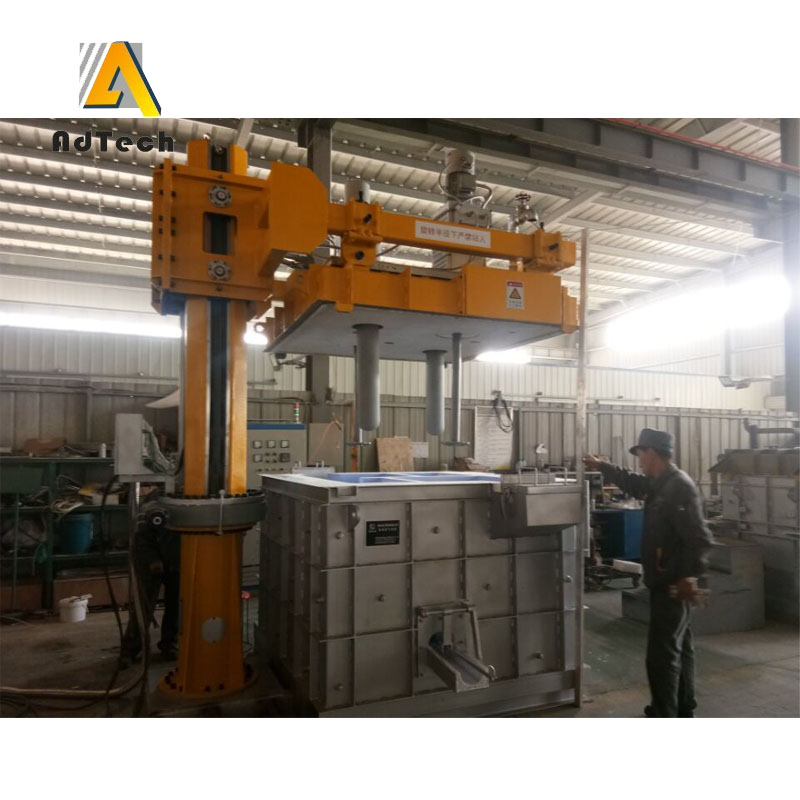
Adtech ONLINE DEGASSING UNIT Instruction
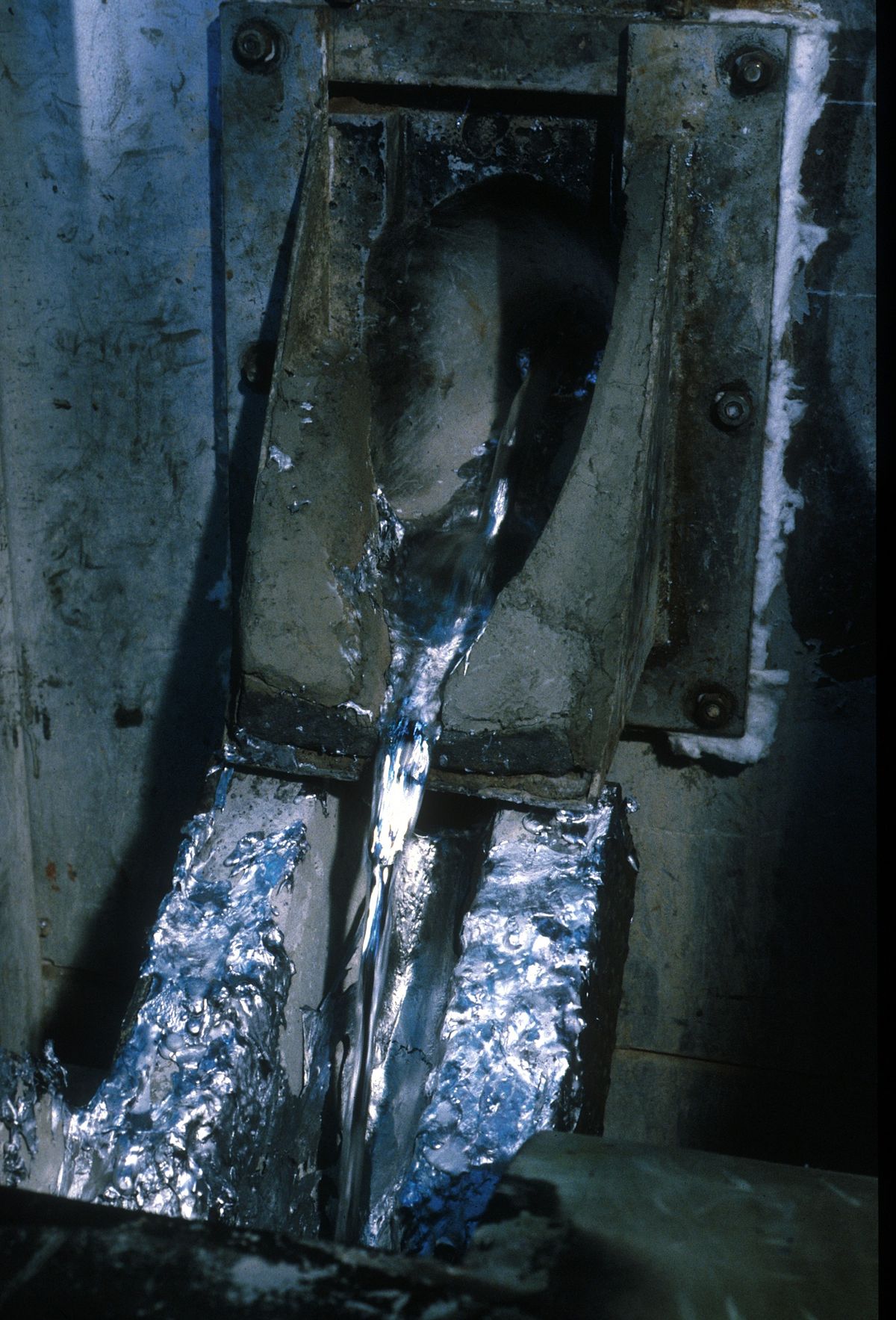
Switch off the heating unit after degassing box heating completed. Guide inert gas into rotor and release molten aluminum into the box when the heater temperature is closed to molten aluminum temperature.
Check the sealing between inlet/outlet and launder.
Check the cone located in heat protection draining in the bottom.
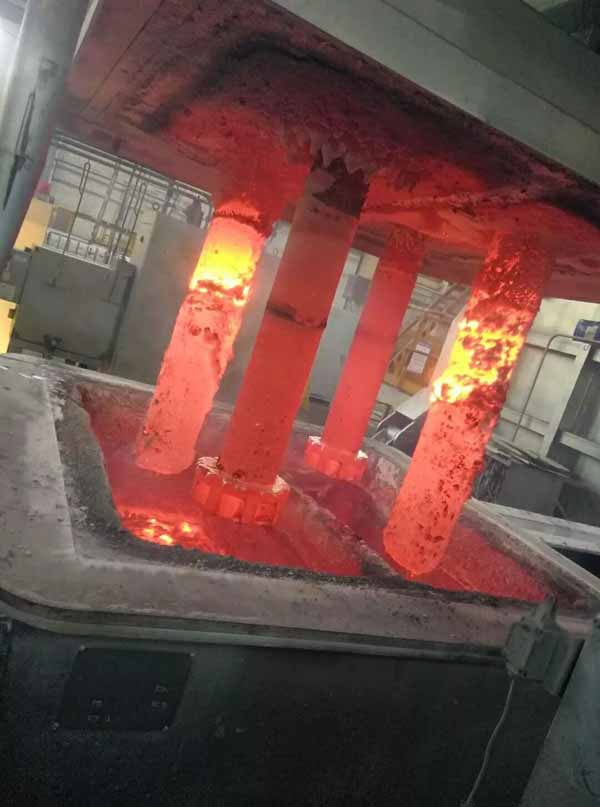
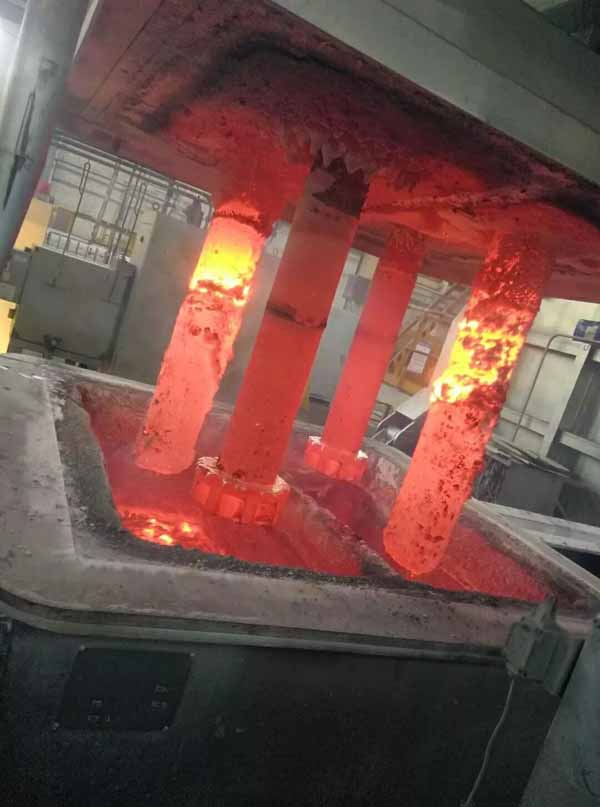
Check the molten aluminum temperature (min 720°C). Make the height of molten aluminum which be away from launder bottom at 3cm for observing the molten aluminum going into the box.
Operator shall wear protection clothes to close the cover. The slag on surface can be skimmed through the deslagging outlet when the molten aluminum flows into the box.
Start production when temperature up to 780°C. Close deslagging outlet for heating preservation.
Molten aluminum can be retained in the box with setting temperature during the heat preservation phase but with no molten aluminum handling.
Guide inert gases into the rotor to prevent air outlet blocking by molten aluminum.
Switch on the heater as soon as molten aluminum flow into the box completed and set heat preservation parameters.
Starting the heating system, control the temperature of the molten aluminum, monitor the gas flow rate, the speed of the rotor is changed from the heat preservation stage to the processing stage. At the same time, the inert gas flow into the rotor increases and the gas flow rate is changed from the preservation stage to the processing stage.
Operator sets molten aluminum heating temperature, maintain a stable degassing working condition.













Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.