
14 10月 Aluminium Degassing Process In Casting
Aluminium Degassing Process In Casting can greatly improve the quality and yield of aluminum products, thereby increasing the profitability of aluminum melting and casting plants.
Aluminium Degassing manufacturer Adtech explained the reason for H in aluminum melt in this way.
Hydrogen can be burned in a gas furnace, condensate on the tool, flux and alloy additives are introduced into the liquid aluminum.
However, most commonly, hydrogen is introduced into molten aluminum through atmospheric humidity. The solubility of hydrogen increases with the relative humidity of the atmosphere.
Given its light weight, aluminum is a metal that is often used for its relative strength.
However, when casting aluminum, impurities called inclusions can create weak points in the product.
There are many reasons for these inclusions, but the presence of hydrogen is one of the most common.
Hydrogen is soluble in liquid aluminum, and it can pass through molten aluminum almost as easily as air.
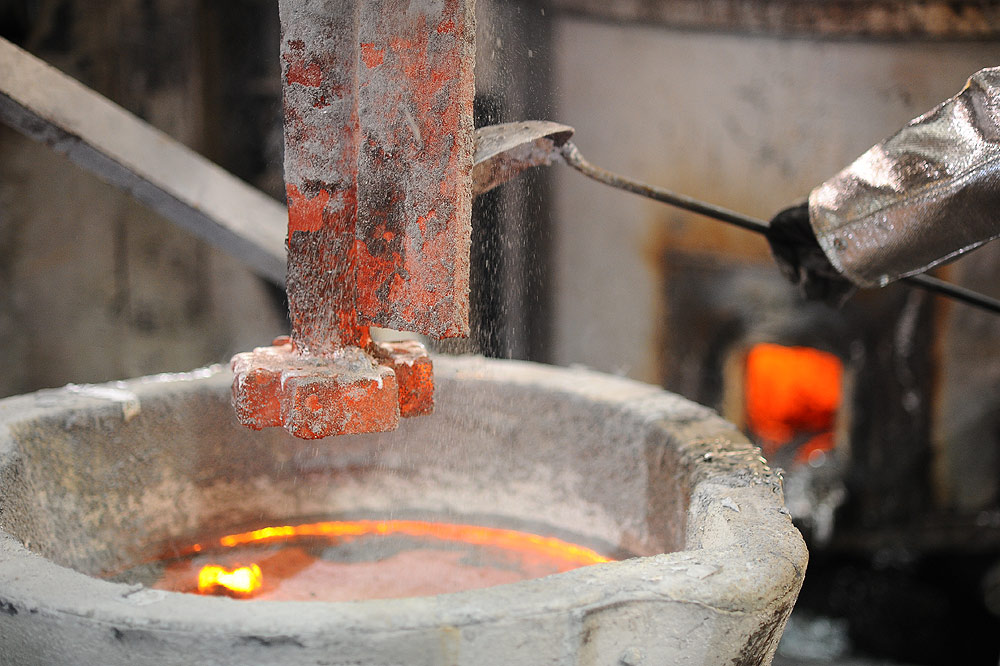
As the liquid metal cools and hardens, hydrogen flows from the high-pressure area to the low-pressure area.
It coalesces and produces gas pockets, which become inclusions and weak points when the metal solidifies.
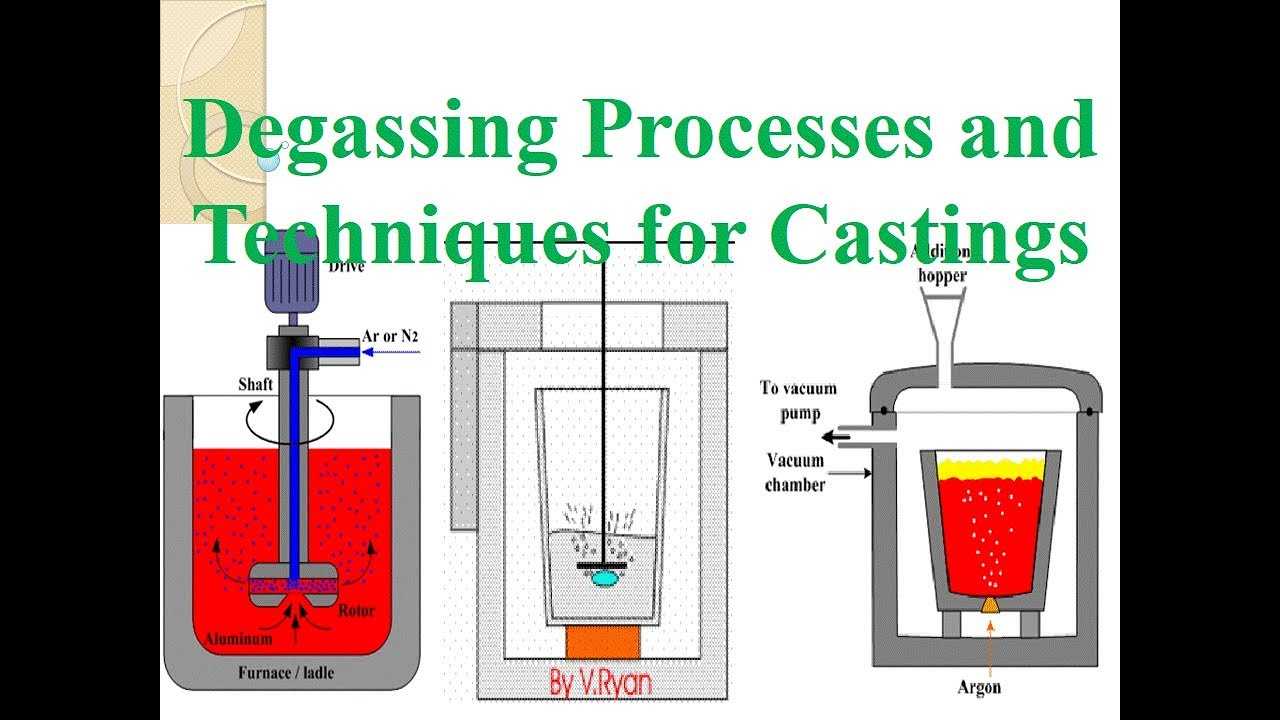
Aluminium Degassing Process In Casting is a process used to remove hydrogen from molten aluminum.

Removal process
As the demand for high-quality aluminum products increases, especially in the aerospace industry, the need to reduce inclusions in molded products also increases.
A popular method of removing hydrogen involves introducing blown nitrogen into liquid aluminum.
The hydrogen is attracted to the nitrogen bubbles, then absorbed by the aluminum and released to the surface.
Argon gas is also very effective, but due to the high cost associated with this gas, nitrogen is preferred.
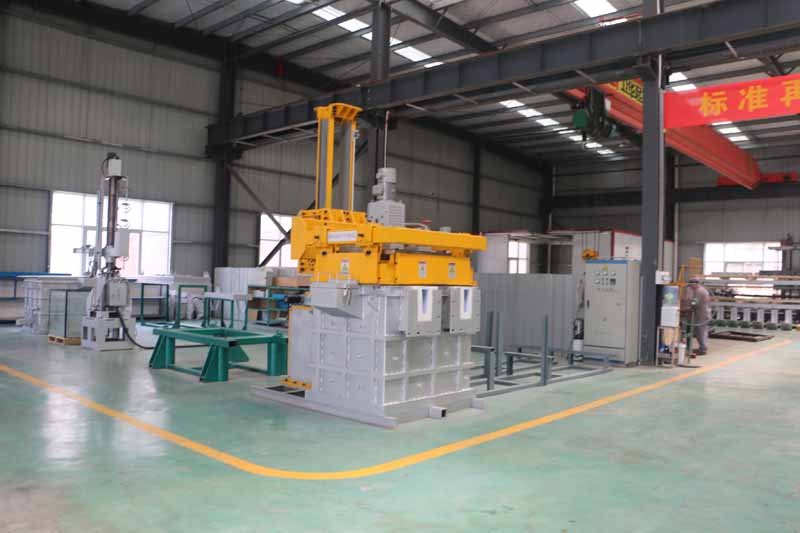
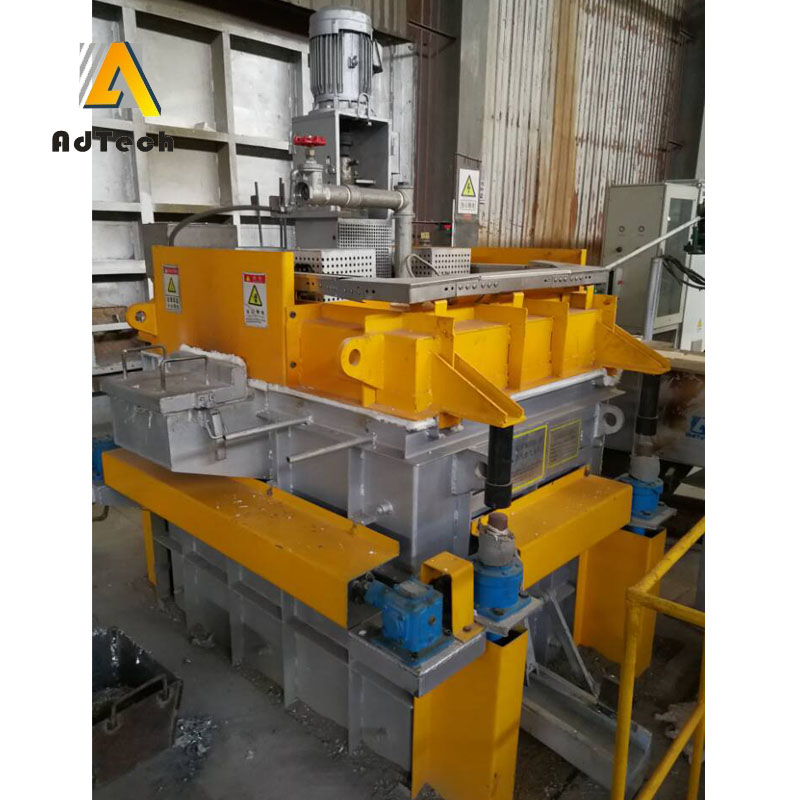
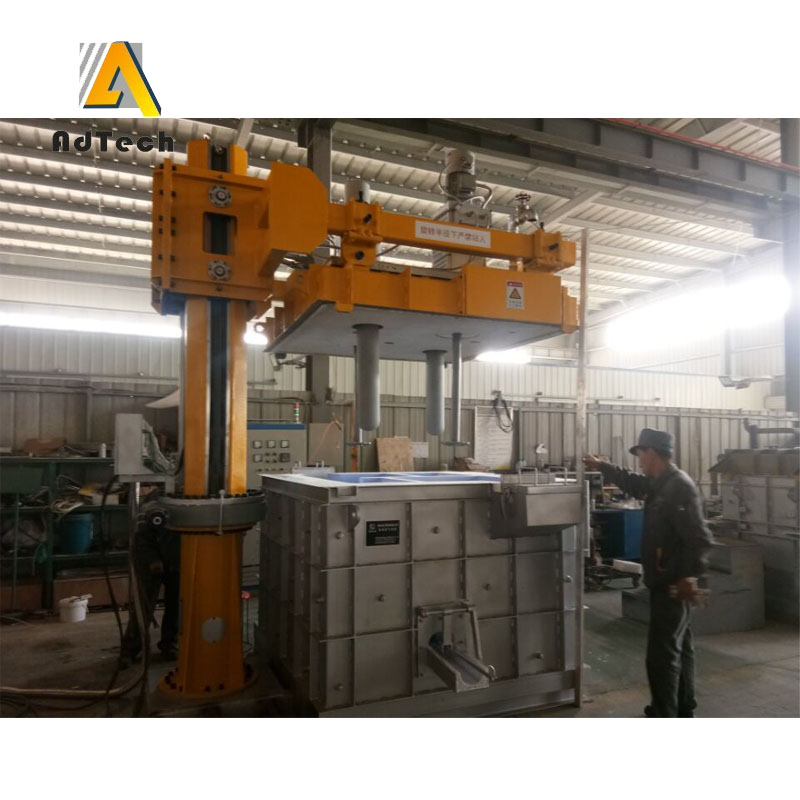
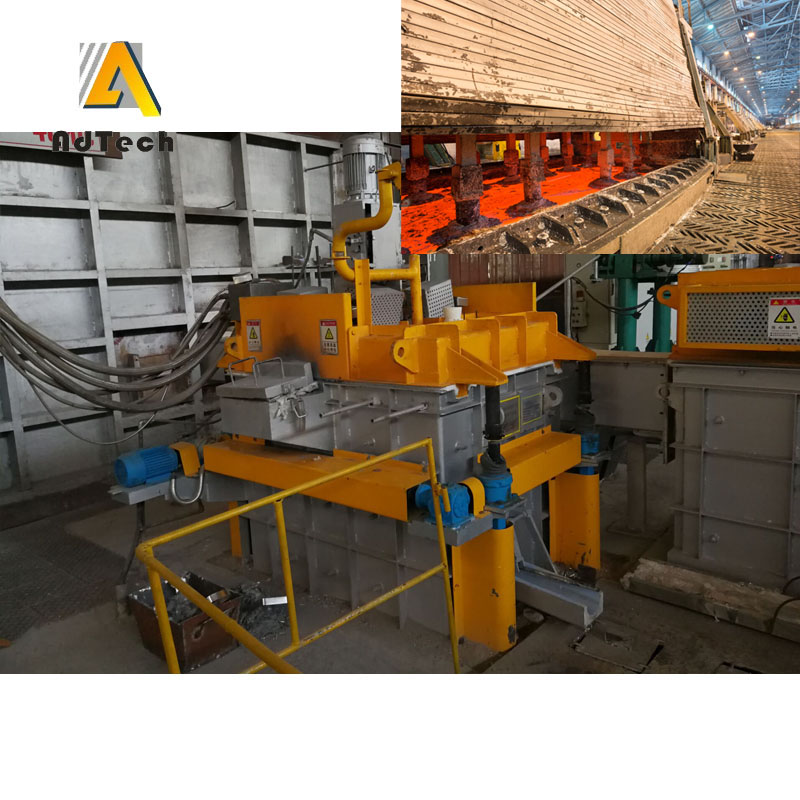
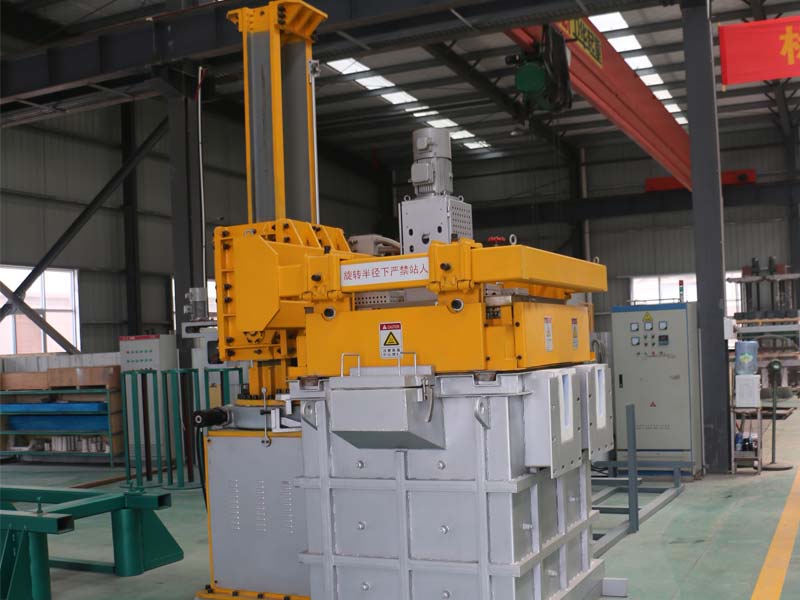
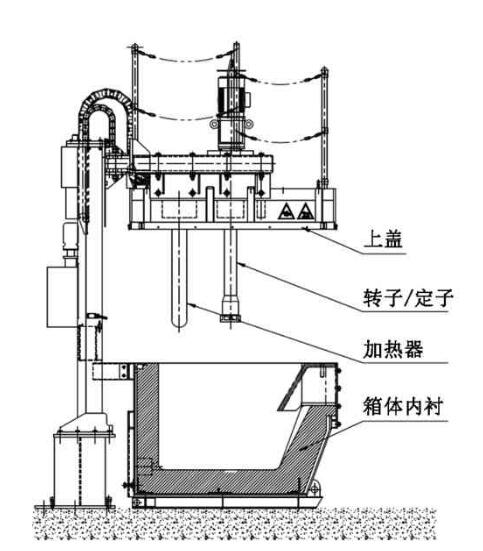
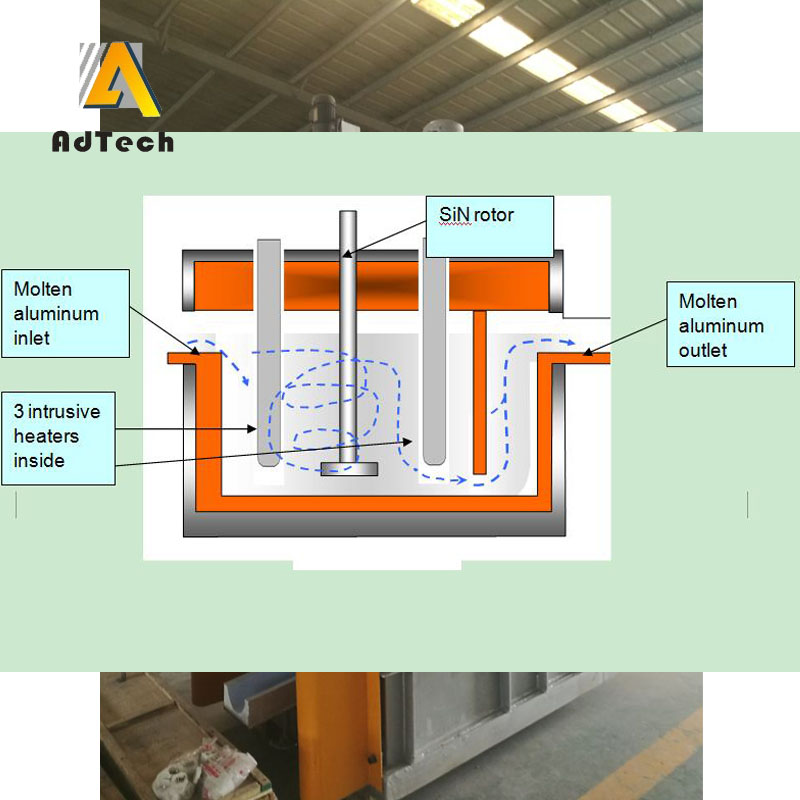
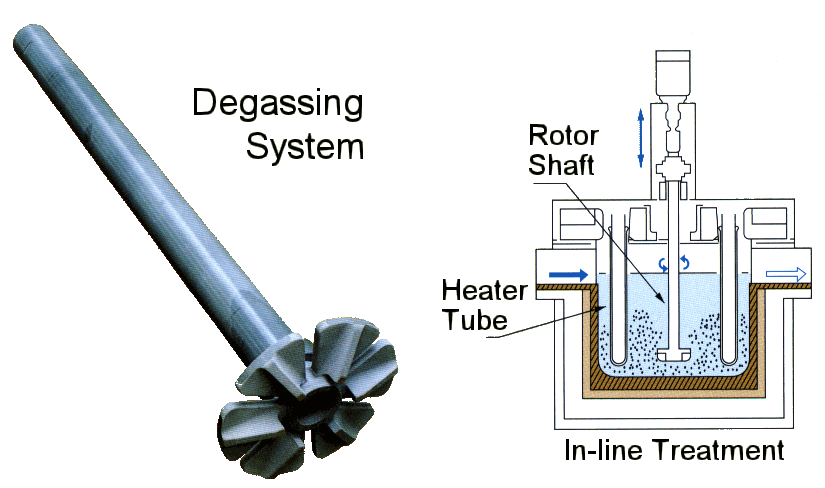
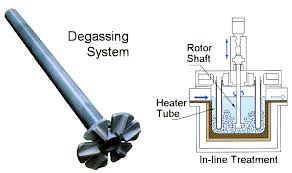
Rotating Degassing Unit
The rotating impeller works by increasing the surface area of the inert gas introduced into the metal.
The smaller nitrogen bubbles produced by the impeller process have a larger total surface area and collect more hydrogen.
The lower surface disturbance of the smaller bubbles also allows less hydrogen to be recaptured into the metal from atmospheric moisture.
Aluminium Degassing Process In Casting, through the rotating shaft and rotor to remove inert or chemically inert gases (argon, nitrogen).
The energy of the rotating shaft results in the formation of a large number of small bubbles, which provides a very high surface area to volume ratio.
The large surface area promotes the rapid and effective diffusion of hydrogen into the bubbles, thereby equalizing the hydrogen activity in the liquid and gas phases.
Compared with flux degassing, rotary degassing machines can remove hydrogen more thoroughly.
In addition, the rotary degasser does not use harmful chlorine and fluoride salts.
Rotary degassing machine can also combine degassing and flux introduction functions.
In this case, the inert gas acts as a carrier for the granular flux. This method is called flux injection.












Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.